Post
MPU6050 (Accelerometer+Gyroscope) Interfacing with Raspberry Pi
MPU6050 (Accelerometer+Gyroscope) Interfacing with Raspberry Pi
Introduction
- MPU6050 sensor module is an integrated 6-axis Motion tracking device.
- It has a 3-axis Gyroscope, 3-axis Accelerometer, Digital Motion Processor and a Temperature sensor, all in a single IC.
- It can accept inputs from other sensors like 3-axis magnetometer or pressure sensor using its Auxiliary I2C bus.
- If external 3-axis magnetometer is connected, it can provide complete 9-axis Motion Fusion output.
- A microcontroller can communicate with this module using I2C communication protocol. Various parameters can be found by reading values from addresses of certain registers using I2C communication.
- Gyroscope and accelerometer reading along X, Y and Z axes are available in 2’s complement form.
- Gyroscope readings are in degrees per second (dps) unit; Accelerometer readings are in g unit.
For more information about MPU6050 Sensor Module and how to use it, refer the topic MPU6050 Sensor Module in the sensors and modules section.
To interface MPU6050 using Raspberry Pi, we should ensure that I2C protocol on Raspberry Pi is turned on. So before going for interfacing MPU6050 with raspberry Pi, we need to make some I2C configurations on Raspberry Pi which you can refer Raspberry Pi I2C.
After configuring I2C on Raspberry Pi, let’s interface Raspberry Pi with MPU6050.
Interfacing Diagram
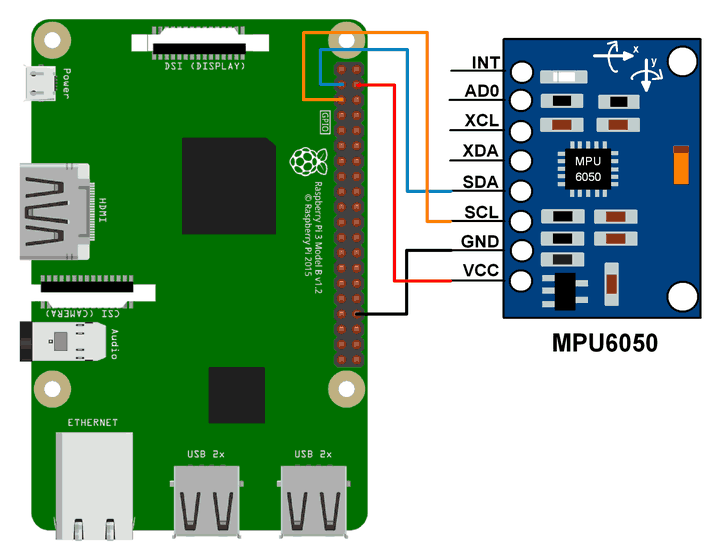
MPU6050 Interfacing with Raspberry Pi
Example
Here, we will interface MPU6050 module with Raspberry Pi to read Gyroscope and Accelerometer value and print them.
We can interface MPU6050 module with Raspberry Pi using Python and C language. We will display the value of Accelerometer and Gyroscope on terminal which are read from MPU6050 module.
For frequently used Python based I2C function on Raspberry Pi you can refer Python based I2C functions for Raspberry Pi.
Python Program
'''
Read Gyro and Accelerometer by Interfacing Raspberry Pi with MPU6050 using Python
http://www.electronicwings.com
'''
import smbus #import SMBus module of I2C
from time import sleep #import
#some MPU6050 Registers and their Address
PWR_MGMT_1 = 0x6B
SMPLRT_DIV = 0x19
CONFIG = 0x1A
GYRO_CONFIG = 0x1B
INT_ENABLE = 0x38
ACCEL_XOUT_H = 0x3B
ACCEL_YOUT_H = 0x3D
ACCEL_ZOUT_H = 0x3F
GYRO_XOUT_H = 0x43
GYRO_YOUT_H = 0x45
GYRO_ZOUT_H = 0x47
def MPU_Init():
#write to sample rate register
bus.write_byte_data(Device_Address, SMPLRT_DIV, 7)
#Write to power management register
bus.write_byte_data(Device_Address, PWR_MGMT_1, 1)
#Write to Configuration register
bus.write_byte_data(Device_Address, CONFIG, 0)
#Write to Gyro configuration register
bus.write_byte_data(Device_Address, GYRO_CONFIG, 24)
#Write to interrupt enable register
bus.write_byte_data(Device_Address, INT_ENABLE, 1)
def read_raw_data(addr):
#Accelero and Gyro value are 16-bit
high = bus.read_byte_data(Device_Address, addr)
low = bus.read_byte_data(Device_Address, addr+1)
#concatenate higher and lower value
value = ((high 8) | low)
#to get signed value from mpu6050
if(value > 32768):
value = value - 65536
return value
bus = smbus.SMBus(1) # or bus = smbus.SMBus(0) for older version boards
Device_Address = 0x68 # MPU6050 device address
MPU_Init()
print (" Reading Data of Gyroscope and Accelerometer")
while True:
#Read Accelerometer raw value
acc_x = read_raw_data(ACCEL_XOUT_H)
acc_y = read_raw_data(ACCEL_YOUT_H)
acc_z = read_raw_data(ACCEL_ZOUT_H)
#Read Gyroscope raw value
gyro_x = read_raw_data(GYRO_XOUT_H)
gyro_y = read_raw_data(GYRO_YOUT_H)
gyro_z = read_raw_data(GYRO_ZOUT_H)
#Full scale range +/- 250 degree/C as per sensitivity scale factor
Ax = acc_x/16384.0
Ay = acc_y/16384.0
Az = acc_z/16384.0
Gx = gyro_x/131.0
Gy = gyro_y/131.0
Gz = gyro_z/131.0
print ("Gx=%.2f" %Gx, u'\u00b0'+ "/s", "\tGy=%.2f" %Gy, u'\u00b0'+ "/s", "\tGz=%.2f" %Gz, u'\u00b0'+ "/s", "\tAx=%.2f g" %Ax, "\tAy=%.2f g" %Ay, "\tAz=%.2f g" %Az)
sleep(1)
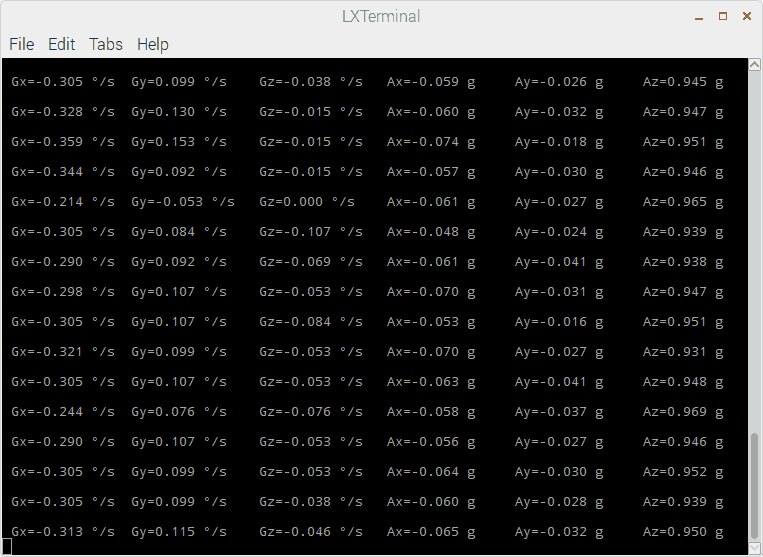
MPU6050 Output
Output window will show all values mentioned below
Gx = Gyro X-axis data in degree/seconds
Gy = Gyro Y-axis data in degree/seconds
Gz = Gyro Z-axis data in degree/seconds
Ax = Accelerometer X-axis data in g
Ay = Accelerometer Y-axis data in g
Az = Accelerometer Z-axis data in g
Supporting Files
- MPU6050 interface with RaspberryPi using Python Download
https://github.com/richardghirst/PiBits/tree/master/ServoBlaster